Don't Fall for Phishing Scams, Here's How
Phishing is the most common form of cyber attack. Your sensitive data can be compromised through just one click if you aren't cautious. Cybercriminals use various channels like email, text message, or malicious websites disguised as trustworthy sources to gain access to systems, steal passwords, or install malware.
At the end of the day, YOU are the last line of defense in a phishing attack. Below is a guide on how to know when you’ve been sent a scam, so you don't accidentally fall victim.
Signs You've Been Emailed a Phishing Cyber Attack:
1. The email says To: & From: with the same address
Sending emails this way is a classic spoofing tactic. This method is used to confuse and bypass spam filters and/or to hide the actual recipient. Since email wasn't designed with strong authentication in mind, it is a common channel for attacks. If you note the same address in the 'To' and 'From' fields, it's a simple way to identify something's up.
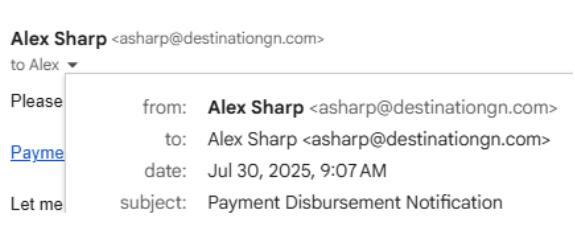
Below is an example of an email we received that was sent "from: Alex Sharp" and "to: Alex Sharp". This is an immediate sign that the email is likely malicious.
2. You receive a Link to a PDF or document instead of an Attachment
If the email were real, a PDF would be sent as an attachment to the email- not as a link to be clicked on. If you are sent a random link, do NOT click on it. Instead, hover over the link, and on the bottom left of your screen, the URL will appear. This way, you can read where the link would have sent you had it been clicked. Try hovering to view a preview of the URL if you receive any questionable attachments or links.
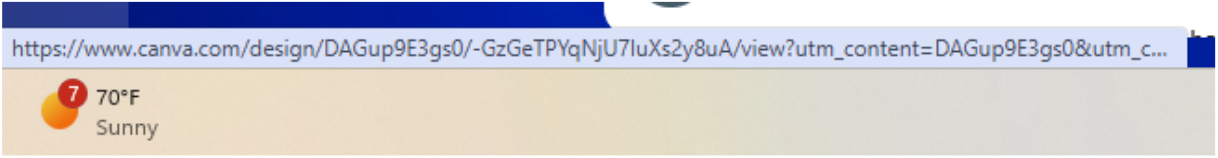
Below is an example of hovering over a link that said PaymentReciept.pdf
This link is NOT what a PDF would normally look like....
3. There is urgency in the nature of the message
Phishing attacks often involve urgency– this could be centered around: payments, signatures, or pertinent messages. A crucial element of phishing scams is causing the victim to rush to engage and interact with the scam. The urgency is meant to trigger a quick response, bypassing time for rational thinking.
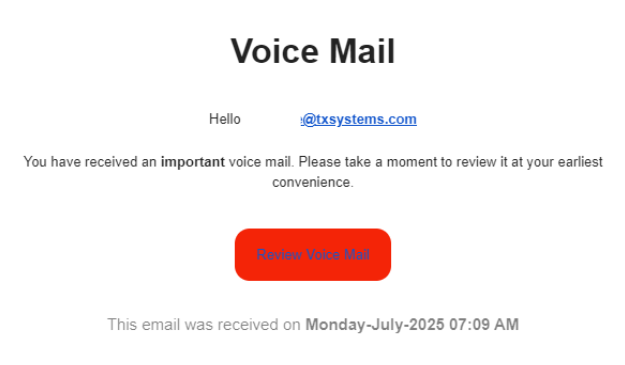
These messages also mimic real situations that you may come across in your work. At first glance, these scams may not seem suspicious because of their similarity to legitimate urgent situations. Below is an example of an email with a link to review a voicemail message that was left. Take note of the text: "review it at your earliest convenience". This is just one example of action-required urgency- it can also come in the form of accessing payment records, giving a signature, etc.
4. Important text has spelling errors
If there is a spelling error in the subject or in other areas of the email, this may be a sign that you received an unauthentic email. Repeated spelling and grammar errors hint towards a suspicious message. This happens for a few reasons. One, deliberately misspelled words can help bypass detection by spam filters. Two, people who do not notice or still engage despite the spelling errors are more likely to fall for the scam all the way through, to giving credentials or paying fake invoices. Three, language and translation issues from attacks based where English is not the native language can contain awkward sentence structure and grammatical errors.
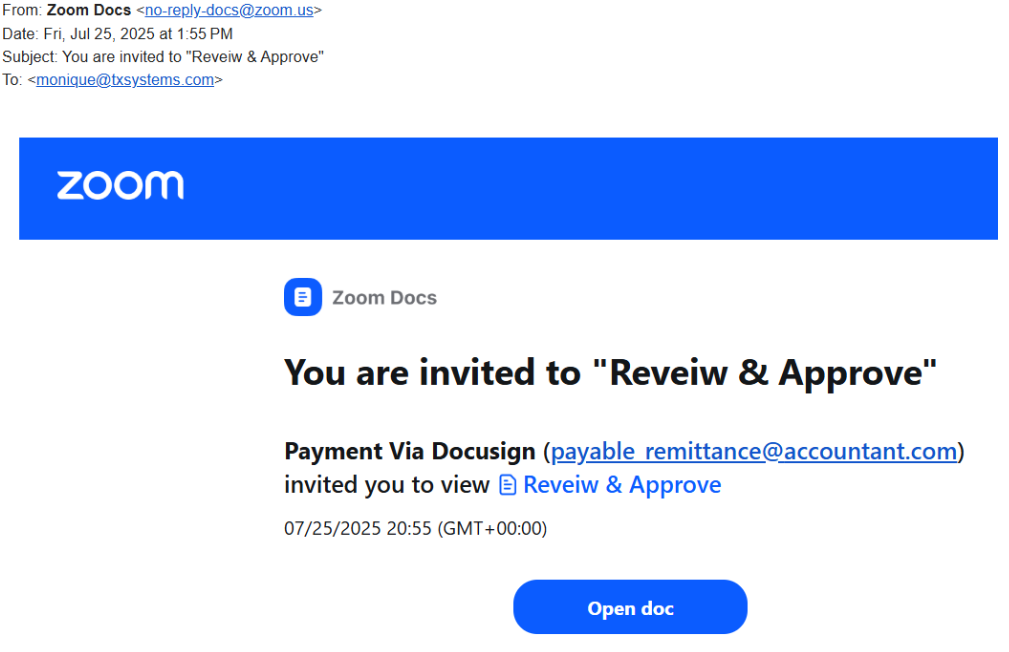
Below is an example of an email that used the company Zoom to appear legitimate. If you are paying attention to the message, the subject and header text "Reveiw & Approve" are misspelled- Reveiw, not Review. The other way to tell this email is malicious is that Zoom does not have a DocuSign or deal with documents.
Always Determine if You've Been Sent Harmful Spam
Attacks can come from many angles. Here are a few examples that we've been sent in the last few months:
- Impersonating well-known companies, like Zoom or DocuSign
- Impersonating a customer or vendor with a payment attachment or request
- Impersonating a co-worker needing information (the email address is a tell-tale sign)
- Notifying that an urgent message is waiting in your voicemail inbox
- Notifying that you have documents to review or approve
To easily determine if you've been sent an attack:
- You can (and should) reference any of the tips listed in this document. #1 and #2 are particularly fast ways to determine if you've been sent a harmful message.
- If you are still unsure, copy and paste the whole email into ChatGPT or another AI. In the prompt, ask if the email is spam. This is a good method to use for verification when you are unsure.
When in doubt, DON’T click.